| 500 Pruta Israel (1948 - ... > History > Difference |
| Revision date | 2018-05-09 03:25 (older) | 2024-04-02 16:20 (newer) |
| Posted by | ||
| Revision status | Verified | Verified |
-300-150-smcKX9IS9m8AAAFYH3a66752.jpg)
|
-300-150-smcKX9IS9m8AAAFYH3a66752.jpg)
|
|
| Denomination | 500 Pruta | 500 Pruta |
| State | Israel (1948 - ) | Israel (1948 - ) |
| Issue year(s) | 1949 | |
| Metal | Silver | Silver |
| Person | ||
| Categories | ||
| Catalog reference | ||
Description -
 English
English
|
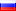
1949, Israeil (Republic). Silver 500 Pruta "Pomegrenade" Coin. Mint Year: 1949 Reference: KM-16. Mintage: 33,812 pcs. Denomination: 500 Pruta Condition: Minor contact-marks and toning spots, otherise UNCirculated! Material: Silver (.500) Weight: 24.95gm Diameter: 37mm
Israel (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; Hebrew: יִשְׂרָאֵל; Arabic: إِسْرَائِيل), officially the State of Israel, is a country in the Middle East, on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea. It has land borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively, and Egypt to the southwest. The country contains geographically diverse features within its relatively small area. Israel's economy and technology center is Tel Aviv, while its seat of government and proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, although the state's sovereignty over Jerusalem is not recognised internationally. The Kingdoms of Israel and Judah emerged during the Iron Age. The Neo-Assyrian Empire destroyed Israel around 720 BCE. Judah was later conquered by the Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic empires and had existed as Jewish autonomous provinces. The successful Maccabean Revolt led to an independent Jewish kingdom in 110 BCE, which came to an end in 63 BCE when the Hasmonean kingdom became a client state of the Roman Republic that subsequently installed the Herodian dynasty in 37 BCE, and in 6 CE created the Roman province of Judea. Judea lasted as a Roman province until the failed Jewish revoltsresulted in widespread destruction, expulsion of Jewish population and the renaming of the region from Iudaea to Syria Palaestina.[28] Jewish presence in the region has persisted to a certain extent over the centuries. In the 7th century the Levant was taken from the Byzantine Empire by the Arabs and remained in Muslim control until the First Crusade of 1099, followed by the Ayyubid conquest of 1187. The Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt extended its control over the Levant in the 13th century until its defeat by the Ottoman Empire in 1517. During the 19th century, national awakening among Jews led to the establishment of the Zionist movement in the diaspora followed by waves of immigration to Ottoman and later British Palestine. In 1947, the United Nations adopted a Partition Plan for Palestine recommending the creation of independent Arab and Jewish states and an internationalized Jerusalem. The plan was accepted by the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and rejected by Arab leaders. The following year, the Jewish Agency declared the independence of the State of Israel, and the subsequent 1948 Arab–Israeli War saw Israel's establishment over most of the former Mandate territory, while the West Bank and Gaza were held by neighboring Arab states. Israel has since fought several wars with Arab countries, and it has since 1967 occupied territories including the West Bank, Golan Heights and the Gaza Strip (still considered occupied after 2005 disengagement, although some legal experts, dispute this claim). It extended its laws to the Golan Heights and East Jerusalem, but not the West Bank. Israel's occupation of the Palestinian territories is the world's longest military occupation in modern times. Efforts to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict have not resulted in peace. However, peace treaties between Israel and both Egypt and Jordan have been signed. In its Basic Laws, Israel defines itself as a Jewish and democratic state. Israel is a representative democracy with a parliamentary system, proportional representation and universal suffrage. The prime ministeris head of government and the Knesset is the legislature. Israel is a developed country and an OECD member, with the 33rd-largest economy in the world by nominal gross domestic product as of 2017. The country benefits from a highly skilled workforce and is among the most educated countries in the world with one of the highest percentages of its citizens holding a tertiary education degree. Israel has the highest standard of living in the Middle East, and has one of the highest life expectancies in the world. |
1949, Israeil (Republic). Silver 500 Pruta "Pomegrenade" Coin. Mint Year: 1949 Reference: KM-16. Mintage: 33,812 pcs. Denomination: 500 Pruta Condition: Minor contact-marks and toning spots, otherise UNCirculated! Material: Silver (.500) Weight: 24.95gm Diameter: 37mm
Israel (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; Hebrew: יִשְׂרָאֵל; Arabic: إِسْرَائِيل), officially the State of Israel, is a country in the Middle East, on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea. It has land borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively, and Egypt to the southwest. The country contains geographically diverse features within its relatively small area. Israel's economy and technology center is Tel Aviv, while its seat of government and proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, although the state's sovereignty over Jerusalem is not recognised internationally. The Kingdoms of Israel and Judah emerged during the Iron Age. The Neo-Assyrian Empire destroyed Israel around 720 BCE. Judah was later conquered by the Babylonian, Persian and Hellenistic empires and had existed as Jewish autonomous provinces. The successful Maccabean Revolt led to an independent Jewish kingdom in 110 BCE, which came to an end in 63 BCE when the Hasmonean kingdom became a client state of the Roman Republic that subsequently installed the Herodian dynasty in 37 BCE, and in 6 CE created the Roman province of Judea. Judea lasted as a Roman province until the failed Jewish revoltsresulted in widespread destruction, expulsion of Jewish population and the renaming of the region from Iudaea to Syria Palaestina.[28] Jewish presence in the region has persisted to a certain extent over the centuries. In the 7th century the Levant was taken from the Byzantine Empire by the Arabs and remained in Muslim control until the First Crusade of 1099, followed by the Ayyubid conquest of 1187. The Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt extended its control over the Levant in the 13th century until its defeat by the Ottoman Empire in 1517. During the 19th century, national awakening among Jews led to the establishment of the Zionist movement in the diaspora followed by waves of immigration to Ottoman and later British Palestine. In 1947, the United Nations adopted a Partition Plan for Palestine recommending the creation of independent Arab and Jewish states and an internationalized Jerusalem. The plan was accepted by the Jewish Agency for Palestine, and rejected by Arab leaders. The following year, the Jewish Agency declared the independence of the State of Israel, and the subsequent 1948 Arab–Israeli War saw Israel's establishment over most of the former Mandate territory, while the West Bank and Gaza were held by neighboring Arab states. Israel has since fought several wars with Arab countries, and it has since 1967 occupied territories including the West Bank, Golan Heights and the Gaza Strip (still considered occupied after 2005 disengagement, although some legal experts, dispute this claim). It extended its laws to the Golan Heights and East Jerusalem, but not the West Bank. Israel's occupation of the Palestinian territories is the world's longest military occupation in modern times. Efforts to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict have not resulted in peace. However, peace treaties between Israel and both Egypt and Jordan have been signed. In its Basic Laws, Israel defines itself as a Jewish and democratic state. Israel is a representative democracy with a parliamentary system, proportional representation and universal suffrage. The prime ministeris head of government and the Knesset is the legislature. Israel is a developed country and an OECD member, with the 33rd-largest economy in the world by nominal gross domestic product as of 2017. The country benefits from a highly skilled workforce and is among the most educated countries in the world with one of the highest percentages of its citizens holding a tertiary education degree. Israel has the highest standard of living in the Middle East, and has one of the highest life expectancies in the world. |
Description -
 Deutsch
Deutsch
|
1949, Israel (Republik). Silberne 500-Pruta-Münze „Granatgranate“. Prägejahr: 1949 Referenz: KM-16. Auflage: 33.812 Stück. Nennwert: 500 Pruta Zustand: Kleinere Kontaktspuren und Tönungsflecken, ansonsten unzirkuliert! Material: Silber (.500) Gewicht: 24,95 g Durchmesser: 37 mm Israel (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; Hebräisch: יִשְׂרָאֵל; Arabisch: إِسْرَائِيل), offiziell der Staat Israel, ist ein Land im Nahen Osten südöstliches Ufer des Mittelmeers und nördliches Ufer des Roten Meeres. Es grenzt im Norden an den Libanon, im Nordosten an Syrien, im Osten an Jordanien, im Osten bzw. Westen an die palästinensischen Gebiete im Westjordanland und im Gazastreifen sowie im Südwesten an Ägypten. Das Land weist auf seinem relativ kleinen Gebiet geografisch unterschiedliche Merkmale auf. Israels Wirtschafts- und Technologiezentrum ist Tel Aviv, während sein Regierungssitz und seine proklamierte Hauptstadt Jerusalem sind, obwohl die Souveränität des Staates über Jerusalem international nicht anerkannt wird. Die Königreiche Israel und Juda entstanden während der Eisenzeit. Das Neuassyrische Reich zerstörte Israel um 720 v. Chr. Juda wurde später von den babylonischen, persischen und hellenistischen Reichen erobert und existierte als jüdische autonome Provinzen. Der erfolgreiche Makkabäer-Aufstand führte 110 v. Chr. zu einem unabhängigen jüdischen Königreich, das 63 v. Chr. zu Ende ging, als das hasmonäische Königreich ein Vasallenstaat der Römischen Republik wurde, die anschließend 37 v. Chr. die Herodianische Dynastie einführte und im Jahr 6 n. Chr. gründete Römische Provinz Judäa. Judäa blieb eine römische Provinz, bis die gescheiterten jüdischen Aufstände zu weitreichenden Zerstörungen, der Vertreibung der jüdischen Bevölkerung und der Umbenennung der Region von Iudaea in Syrien-Palästina führten.[28] Die jüdische Präsenz in der Region blieb über die Jahrhunderte bis zu einem gewissen Grad bestehen. Im 7. Jahrhundert wurde die Levante von den Arabern dem Byzantinischen Reich entrissen und blieb bis zum Ersten Kreuzzug von 1099 unter muslimischer Kontrolle, gefolgt von der Eroberung durch die Ayyubiden im Jahr 1187. Das Mamluken-Sultanat Ägypten weitete seine Kontrolle über die Levante im 13. Jahrhundert aus bis zu seiner Niederlage gegen das Osmanische Reich im Jahr 1517. Im 19. Jahrhundert führte das nationale Erwachen unter den Juden zur Gründung der zionistischen Bewegung in der Diaspora, gefolgt von Einwanderungswellen ins osmanische und später britische Palästina. 1947 verabschiedeten die Vereinten Nationen einen Teilungsplan für Palästina, der die Schaffung unabhängiger arabischer und jüdischer Staaten und eines internationalisierten Jerusalems empfahl. Der Plan wurde von der Jewish Agency for Palestine angenommen und von arabischen Führern abgelehnt. Im folgenden Jahr erklärte die Jewish Agency die Unabhängigkeit des Staates Israel, und im darauffolgenden Arabisch-Israelischen Krieg von 1948 eroberte Israel den größten Teil des ehemaligen Mandatsgebiets, während das Westjordanland und der Gazastreifen von benachbarten arabischen Staaten gehalten wurden. Seitdem hat Israel mehrere Kriege mit arabischen Ländern geführt und seit 1967 Gebiete besetzt, darunter das Westjordanland, die Golanhöhen und den Gazastreifen (der nach dem Abzug von 2005 immer noch als besetzt gilt, obwohl einige Rechtsexperten diese Behauptung bestreiten). Es dehnte seine Gesetze auf die Golanhöhen und Ostjerusalem aus, nicht jedoch auf das Westjordanland. Die Besetzung der palästinensischen Gebiete durch Israel ist die längste militärische Besetzung der Welt in der Neuzeit. Bemühungen zur Lösung des israelisch-palästinensischen Konflikts haben nicht zu Frieden geführt. Allerdings wurden Friedensverträge zwischen Israel und sowohl Ägypten als auch Jordanien unterzeichnet. In seinen Grundgesetzen definiert sich Israel als jüdischer und demokratischer Staat. Israel ist eine repräsentative Demokratie mit einem parlamentarischen System, Verhältniswahlrecht und allgemeinem Wahlrecht. Der Premierminister ist Regierungschef und die Knesset ist die Legislative. Israel ist ein entwickeltes Land und Mitglied der OECD. Gemessen am nominalen Bruttoinlandsprodukt (Stand 2017) war Israel die 33. größte Volkswirtschaft der Welt. Das Land verfügt über hochqualifizierte Arbeitskräfte und gehört mit einem der am besten ausgebildeten Länder der Welt zu den Ländern Der höchste Prozentsatz der Bürger verfügt über einen Hochschulabschluss. Israel hat den höchsten Lebensstandard im Nahen Osten und eine der höchsten Lebenserwartungen der Welt. |
|
Description -
 Русский
Русский
|
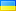
1949 г., Израиль (Республика). Серебряная монета 500 Прута "Гранат". Год монетного двора: 1949 Артикул: КМ-16. Тираж: 33 812 шт. Номинал: 500 Прута Состояние: Незначительные потертости и тонировки, прочее НЕ В РАБОТЕ! Материал: Серебро (.500) Вес: 24,95 г Диаметр: 37 мм Израиль (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; иврит: יִשְׂרָאֵל; арабский: إِسْرَائِيل), официальное государство Израиль, страна на Ближнем Востоке, на юго-восточный берег Средиземного моря и северный берег Красного моря. Он имеет сухопутные границы с Ливаном на севере, Сирией на северо-востоке, Иорданией на востоке, палестинскими территориями Западного берега и сектора Газа на востоке и западе соответственно, а также с Египтом на юго-западе. Страна содержит географически разнообразные объекты на своей относительно небольшой территории. Экономика и технологический центр Израиля — Тель-Авив, а резиденция правительства и провозглашенная столица — Иерусалим, хотя суверенитет государства над Иерусалимом не признан на международном уровне. Царства Израиля и Иудеи возникли в железном веке. Неоассирийская империя уничтожила Израиль около 720 г. до н.э. Позднее Иудея была завоевана Вавилонской, Персидской и Эллинистической империями и существовала как еврейские автономные провинции. Успешное восстание Маккавеев привело к созданию независимого еврейского царства в 110 г. до н. э., которое прекратилось в 63 г. до н. э., когда Хасмонейское царство стало государством-клиентом Римской республики, которая впоследствии установила династию Ирода в 37 г. до н. э., а в 6 г. н. э. создала Римская провинция Иудея. Иудея просуществовала как римская провинция до тех пор, пока неудавшиеся еврейские восстания не привели к массовым разрушениям, изгнанию еврейского населения и переименованию региона из Иудеи в Сирию Палестину.[28] Еврейское присутствие в регионе в определенной степени сохранялось на протяжении веков. В VII веке Левант был захвачен арабами у Византийской империи и оставался под контролем мусульман до Первого крестового похода 1099 года, за которым последовало завоевание Айюбидов в 1187 году. Египетский султанат мамлюков расширил свой контроль над Левантом в 13 веке. до ее поражения от Османской империи в 1517 году. В 19 веке национальное пробуждение среди евреев привело к созданию сионистского движения в диаспоре, за которым последовали волны иммиграции в Османскую, а затем и Британскую Палестину. В 1947 году Организация Объединенных Наций приняла План раздела Палестины, рекомендовавший создание независимых арабского и еврейского государств и интернационализированного Иерусалима. План был принят Еврейским агентством Палестины и отвергнут арабскими лидерами. В следующем году Еврейское агентство провозгласило независимость Государства Израиль, и последующая арабо-израильская война 1948 года привела к установлению Израиля на большей части территории бывшего мандата, в то время как Западный Берег и сектор Газа находились под контролем соседних арабских государств. С тех пор Израиль вел несколько войн с арабскими странами, а с 1967 года оккупировал территории, включая Западный Берег, Голанские высоты и сектор Газа (до сих пор считающиеся оккупированными после размежевания в 2005 году, хотя некоторые эксперты по правовым вопросам оспаривают это утверждение). Оно распространило свои законы на Голанские высоты и Восточный Иерусалим, но не на Западный берег. Оккупация Израилем палестинских территорий является самой длительной военной оккупацией в мире в наше время. Усилия по разрешению израильско-палестинского конфликта не привели к миру. Однако мирные договоры между Израилем, Египтом и Иорданией были подписаны. В своих Основных законах Израиль определяет себя как еврейское и демократическое государство. Израиль является представительной демократией с парламентской системой, пропорциональным представительством и всеобщим избирательным правом. Премьер-министр является главой правительства, а Кнессет является законодательным органом. Израиль является развитой страной и членом ОЭСР, занимая 33-е место по величине экономики в мире по номинальному валовому внутреннему продукту по состоянию на 2017 год. Страна располагает высококвалифицированной рабочей силой и входит в число самых образованных стран мира с одним из самый высокий процент граждан, имеющих высшее образование. В Израиле самый высокий уровень жизни на Ближнем Востоке и одна из самых высоких продолжительностей жизни в мире. |
|
Description -
 Українська
Українська
|
1949, Ізраїль (республіка). Срібна монета Прута 500 проби "Гранат". Рік карбування: 1949 Посилання: KM-16. Тираж: 33 812 шт. Номінал: 500 Прута. Стан: незначні сліди від контакту та плями тонування, за винятком того, що не в обігу! Матеріал: срібло (.500) Вага: 24,95 г Діаметр: 37 мм Ізраїль (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; іврит: יִשְׂרָאֵל; араб.: إِسْرَائِيل), офіційна назва Держава Ізраїль, є країною на Близькому Сході, на південно-східний берег Середземного моря і північний берег Червоного моря. Вона має сухопутні кордони з Ліваном на півночі, Сирією на північному сході, Йорданією на сході, палестинськими територіями Західного берега і сектором Газа на сході та заході, відповідно, і Єгиптом на південному заході. Країна містить географічно різноманітні особливості на своїй відносно невеликій території. Економічний і технологічний центр Ізраїлю — Тель-Авів, а резиденція уряду та проголошена столиця — Єрусалим, хоча державний суверенітет над Єрусалимом не визнаний на міжнародному рівні. Ізраїльське та Юдейське царства виникли в епоху залізного віку. Новоассирійська імперія знищила Ізраїль близько 720 року до нашої ери. Пізніше Юдея була завойована Вавилонською, Перською та Елліністичною імперіями та існувала як єврейська автономна провінція. Успішне повстання Маккавеїв призвело до незалежного єврейського царства в 110 р. до н. е., якому прийшов кінець у 63 р. до н. Римська провінція Юдея. Юдея існувала як римська провінція до тих пір, поки невдалі єврейські повстання призвели до масового руйнування, вигнання єврейського населення та перейменування регіону з Іудеї на Сирію Палестину.[28] Єврейська присутність у регіоні певною мірою зберігалася протягом століть. У 7 столітті Левант був відібраний арабами у Візантійської імперії та залишався під контролем мусульман до Першого хрестового походу 1099 року, за яким послідувало завоювання Айюбідами 1187 року. Єгипетський султанат мамлюків поширив свій контроль над Левантом у 13 столітті до її поразки від Османської імперії в 1517 році. Протягом 19-го століття національне пробудження серед євреїв призвело до заснування сіоністського руху в діаспорі, за яким послідували хвилі імміграції до Османської і пізніше Британської Палестини. У 1947 році Організація Об'єднаних Націй прийняла План поділу Палестини, в якому рекомендувалося створити незалежні арабські та єврейські держави та інтернаціоналізований Єрусалим. План був прийнятий Єврейським агентством для Палестини та відхилений арабськими лідерами. Наступного року Єврейське агентство проголосило незалежність Держави Ізраїль, а наступна арабо-ізраїльська війна 1948 року привела до встановлення Ізраїлю більшої частини колишньої підмандатної території, тоді як Західний берег і Газа утримувалися сусідніми арабськими державами. З тих пір Ізраїль вів кілька воєн з арабськими країнами, і з 1967 року він окупував території, включаючи Західний берег, Голанські висоти та сектор Газа (все ще вважаються окупованими після розмежування в 2005 році, хоча деякі юридичні експерти заперечують це твердження). Він поширив свої закони на Голанські висоти та Східний Єрусалим, але не на Західний берег. Окупація Ізраїлем палестинських територій є найтривалішою військовою окупацією в світі за сучасність. Спроби вирішити ізраїльсько-палестинський конфлікт не привели до миру. Проте мирні договори між Ізраїлем, Єгиптом і Йорданією були підписані. У своїх Основних законах Ізраїль визначає себе як єврейську і демократичну державу. Ізраїль є представницькою демократією з парламентською системою, пропорційним представництвом і загальним виборчим правом. Прем'єр-міністр є головою уряду, а Кнесет є законодавчим органом. Ізраїль є розвиненою країною та членом ОЕСР із 33-ю найбільшою економікою у світі за номінальним валовим внутрішнім продуктом станом на 2017 рік. Країна має висококваліфіковану робочу силу та є однією з найосвіченіших країн світу з одним із найвищий відсоток громадян із вищою освітою. В Ізраїлі найвищий рівень життя на Близькому Сході та одна з найвищих у світі середня тривалість життя. |
|
Description -
 Italiano
Italiano
|
1949, Israele (Repubblica). Moneta "Melograno" in argento da 500 Pruta. Anno di menta: 1949 Riferimento: KM-16. Tiratura: 33.812 pz. Denominazione: 500 Pruta Condizioni: lievi segni di contatto e macchie di viraggio, altrimenti NON Circolata! Materiale: Argento (.500) Peso: 24,95 g Diametro: 37 mm Israele (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; ebraico: יִשְׂרָאֵל; arabo: إِسْرَائِيل), ufficialmente lo Stato di Israele, è un paese del Medio Oriente, sul sponda sudorientale del Mar Mediterraneo e sponda settentrionale del Mar Rosso. Confina con il Libano a nord, con la Siria a nord-est, con la Giordania a est, con i territori palestinesi della Cisgiordania e della Striscia di Gaza rispettivamente a est e a ovest, e con l'Egitto a sud-ovest. Il paese contiene caratteristiche geograficamente diverse all'interno della sua area relativamente piccola. Il centro economico e tecnologico di Israele è Tel Aviv, mentre la sede del governo e la capitale proclamata è Gerusalemme, sebbene la sovranità dello stato su Gerusalemme non sia riconosciuta a livello internazionale. I regni di Israele e Giuda emersero durante l'età del ferro. L'impero neo-assiro distrusse Israele intorno al 720 a.C. Giuda fu successivamente conquistata dagli imperi babilonese, persiano ed ellenistico ed esisteva come province autonome ebraiche. La vittoriosa rivolta dei Maccabei portò alla nascita di un regno ebraico indipendente nel 110 a.C., che terminò nel 63 a.C. quando il regno asmoneo divenne uno stato cliente della Repubblica Romana che successivamente insediò la dinastia erodiana nel 37 a.C., e nel 6 d.C. Provincia romana della Giudea. La Giudea durò come provincia romana fino a quando le fallite rivolte ebraiche provocarono una distruzione diffusa, l'espulsione della popolazione ebraica e la ridenominazione della regione da Giudea a Siria Palestina.[28] La presenza ebraica nella regione è persistita in una certa misura nel corso dei secoli. Nel VII secolo il Levante fu sottratto all'impero bizantino dagli arabi e rimase sotto il controllo musulmano fino alla prima crociata del 1099, seguita dalla conquista ayyubide del 1187. Il Sultanato mamelucco d'Egitto estese il suo controllo sul Levante nel XIII secolo fino alla sua sconfitta da parte dell'Impero Ottomano nel 1517. Durante il XIX secolo, il risveglio nazionale degli ebrei portò alla fondazione del movimento sionista nella diaspora, seguito da ondate di immigrazione nella Palestina ottomana e successivamente britannica. Nel 1947, le Nazioni Unite adottarono un Piano di spartizione della Palestina che raccomandava la creazione di Stati arabi ed ebrei indipendenti e di una Gerusalemme internazionalizzata. Il piano fu accettato dall’Agenzia Ebraica per la Palestina e respinto dai leader arabi. L'anno successivo, l'Agenzia Ebraica dichiarò l'indipendenza dello Stato di Israele e la successiva guerra arabo-israeliana del 1948 vide l'insediamento di Israele sulla maggior parte del territorio dell'ex Mandato, mentre la Cisgiordania e Gaza erano controllate dai vicini stati arabi. Da allora Israele ha combattuto diverse guerre con i paesi arabi e dal 1967 ha occupato territori tra cui la Cisgiordania, le alture di Golan e la Striscia di Gaza (ancora considerate occupate dopo il disimpegno del 2005, anche se alcuni esperti legali contestano questa affermazione). Ha esteso le sue leggi alle alture di Golan e a Gerusalemme est, ma non alla Cisgiordania. L'occupazione israeliana dei territori palestinesi è l'occupazione militare più lunga del mondo nei tempi moderni. Gli sforzi per risolvere il conflitto israelo-palestinese non hanno portato alla pace. Tuttavia, sono stati firmati trattati di pace tra Israele, Egitto e Giordania. Nelle sue Leggi Fondamentali, Israele si definisce uno Stato ebraico e democratico. Israele è una democrazia rappresentativa con un sistema parlamentare, rappresentanza proporzionale e suffragio universale. Il primo ministro è il capo del governo e la Knesset è l’organo legislativo. Israele è un paese sviluppato e membro dell'OCSE, con la 33a economia più grande del mondo per prodotto interno lordo nominale nel 2017. Il paese beneficia di una forza lavoro altamente qualificata ed è tra i paesi più istruiti al mondo con uno dei paesi più sviluppati percentuale più alta di cittadini in possesso di un titolo di studio terziario. Israele ha il tenore di vita più alto del Medio Oriente e una delle aspettative di vita più alte al mondo. |
|
Description -
 Français
Français
|
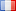
1949, Israël (République). Pièce d'argent 500 Pruta "Grenade". Année neuve : 1949 Référence : KM-16. Tirage : 33 812 pièces. Dénomination : 500 Pruta Condition : Marques de contact mineures et taches tonifiantes, autres NON circulées ! Matériau : Argent (.500) Poids : 24,95 g Diamètre : 37 mm Israël (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/ ; hébreu : יִשְׂרָאֵל ; arabe : إِسْرَائِيل), officiellement l'État d'Israël, est un pays du Moyen-Orient, sur la rive sud-est de la mer Méditerranée et rive nord de la mer Rouge. Il a des frontières terrestres avec le Liban au nord, la Syrie au nord-est, la Jordanie à l'est, les territoires palestiniens de Cisjordanie et de la bande de Gaza à l'est et à l'ouest, respectivement, et l'Égypte au sud-ouest. Le pays présente des caractéristiques géographiques diverses sur une superficie relativement petite. Le centre économique et technologique d'Israël est Tel-Aviv, tandis que le siège de son gouvernement et sa capitale proclamée sont Jérusalem, bien que la souveraineté de l'État sur Jérusalem ne soit pas reconnue au niveau international. Les royaumes d'Israël et de Juda ont émergé pendant l'âge du fer. L’Empire néo-assyrien a détruit Israël vers 720 avant notre ère. Juda fut ensuite conquise par les empires babylonien, perse et hellénistique et existait en tant que provinces juives autonomes. La révolte réussie des Maccabées a conduit à un royaume juif indépendant en 110 av. Province romaine de Judée. La Judée est restée une province romaine jusqu'à ce que les révoltes juives ratées entraînent une destruction généralisée, l'expulsion de la population juive et le changement de nom de la région d'Iudaea en Syrie Palaestina. La présence juive dans la région a persisté dans une certaine mesure au fil des siècles. Au VIIe siècle, le Levant fut pris à l'Empire byzantin par les Arabes et resta sous contrôle musulman jusqu'à la première croisade de 1099, suivie de la conquête ayyoubide de 1187. Le sultanat mamelouk d'Égypte étendit son contrôle sur le Levant au XIIIe siècle. jusqu'à sa défaite face à l'Empire ottoman en 1517. Au cours du XIXe siècle, le réveil national des Juifs a conduit à l'établissement du mouvement sioniste dans la diaspora, suivi de vagues d'immigration vers la Palestine ottomane, puis britannique. En 1947, les Nations Unies ont adopté un plan de partage de la Palestine recommandant la création d’États arabes et juifs indépendants et d’une Jérusalem internationalisée. Le plan a été accepté par l’Agence juive pour la Palestine et rejeté par les dirigeants arabes. L'année suivante, l'Agence juive a déclaré l'indépendance de l'État d'Israël, et la guerre israélo-arabe de 1948 a vu l'établissement d'Israël sur la majeure partie de l'ancien territoire sous mandat, tandis que la Cisjordanie et Gaza étaient détenues par les États arabes voisins. Depuis lors, Israël a mené plusieurs guerres avec des pays arabes et a occupé depuis 1967 des territoires tels que la Cisjordanie, le plateau du Golan et la bande de Gaza (toujours considérés comme occupés après le désengagement de 2005, bien que certains juristes contestent cette affirmation). Il a étendu ses lois aux hauteurs du Golan et à Jérusalem-Est, mais pas à la Cisjordanie. L'occupation des territoires palestiniens par Israël est la plus longue occupation militaire des temps modernes. Les efforts visant à résoudre le conflit israélo-palestinien n’ont pas abouti à la paix. Cependant, des traités de paix entre Israël, l'Égypte et la Jordanie ont été signés. Dans ses Lois fondamentales, Israël se définit comme un État juif et démocratique. Israël est une démocratie représentative dotée d'un système parlementaire, d'une représentation proportionnelle et du suffrage universel. Le Premier ministre est le chef du gouvernement et la Knesset est le pouvoir législatif. Israël est un pays développé et membre de l'OCDE, avec la 33e économie mondiale en termes de produit intérieur brut nominal en 2017. Le pays bénéficie d'une main-d'œuvre hautement qualifiée et fait partie des pays les plus instruits au monde avec l'un des les pourcentages les plus élevés de ses citoyens sont titulaires d’un diplôme de l’enseignement supérieur. Israël a le niveau de vie le plus élevé du Moyen-Orient et l’une des espérances de vie les plus élevées au monde. |
|
Description -
 Español
Español
|
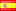
1949, Israel (República). Moneda de Plata de 500 Pruta "Granada". Año de ceca: 1949 Referencia: KM-16. Tirada: 33.812 uds. Denominación: 500 Pruta Condición: Marcas de contacto menores y puntos tonificantes, ¡de lo contrario, sin circular! Material: Plata (.500) Peso: 24,95 g Diámetro: 37 mm Israel (/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/; hebreo: יִשְׂרָאֵל; árabe: إِسْرَائِيل), oficialmente el Estado de Israel, es un país del Medio Oriente, en el costa sureste del Mar Mediterráneo y la costa norte del Mar Rojo. Tiene fronteras terrestres con el Líbano al norte, Siria al noreste, Jordania al este, los territorios palestinos de Cisjordania y la Franja de Gaza al este y oeste, respectivamente, y Egipto al suroeste. El país contiene características geográficamente diversas dentro de su área relativamente pequeña. El centro económico y tecnológico de Israel es Tel Aviv, mientras que su sede de gobierno y capital proclamada es Jerusalén, aunque la soberanía del Estado sobre Jerusalén no está reconocida internacionalmente. Los Reinos de Israel y Judá surgieron durante la Edad del Hierro. El Imperio Neoasirio destruyó Israel alrededor del año 720 a.C. Posteriormente, Judá fue conquistada por los imperios babilónico, persa y helenístico y existió como provincias judías autónomas. La exitosa revuelta macabea condujo a un reino judío independiente en 110 a. C., que llegó a su fin en 63 a. C. cuando el reino asmoneo se convirtió en un estado cliente de la República Romana que posteriormente instaló la dinastía herodiana en 37 a. C., y en 6 d. C. creó la Provincia romana de Judea. Judea duró como provincia romana hasta que las fallidas revueltas judías resultaron en una destrucción generalizada, la expulsión de la población judía y el cambio de nombre de la región de Iudaea a Siria Palaestina. La presencia judía en la región ha persistido hasta cierto punto a lo largo de los siglos. En el siglo VII, los árabes arrebataron el Levante al Imperio bizantino y permaneció bajo control musulmán hasta la Primera Cruzada de 1099, seguida de la conquista ayubí de 1187. El sultanato mameluco de Egipto extendió su control sobre el Levante en el siglo XIII. hasta su derrota por el Imperio Otomano en 1517. Durante el siglo XIX, el despertar nacional entre los judíos condujo al establecimiento del movimiento sionista en la diáspora, seguido de oleadas de inmigración a la Palestina otomana y más tarde a la británica. En 1947, las Naciones Unidas adoptaron un Plan de Partición para Palestina recomendando la creación de estados árabes y judíos independientes y una Jerusalén internacionalizada. El plan fue aceptado por la Agencia Judía para Palestina y rechazado por los líderes árabes. Al año siguiente, la Agencia Judía declaró la independencia del Estado de Israel, y la posterior guerra árabe-israelí de 1948 vio el establecimiento de Israel en la mayor parte del territorio del antiguo Mandato, mientras que Cisjordania y Gaza estaban en manos de estados árabes vecinos. Desde entonces, Israel ha librado varias guerras con países árabes y desde 1967 ha ocupado territorios como Cisjordania, los Altos del Golán y la Franja de Gaza (aún considerados ocupados después de la retirada de 2005, aunque algunos expertos jurídicos cuestionan esta afirmación). Extendió sus leyes a los Altos del Golán y a Jerusalén Este, pero no a Cisjordania. La ocupación israelí de los territorios palestinos es la ocupación militar más larga del mundo en los tiempos modernos. Los esfuerzos por resolver el conflicto palestino-israelí no han dado como resultado la paz. Sin embargo, se han firmado tratados de paz entre Israel y Egipto y Jordania. En sus Leyes Básicas, Israel se define a sí mismo como un Estado judío y democrático. Israel es una democracia representativa con un sistema parlamentario, representación proporcional y sufragio universal. El primer ministro es el jefe de gobierno y la Knesset es el órgano legislativo. Israel es un país desarrollado y miembro de la OCDE, con la 33ª economía más grande del mundo por producto interno bruto nominal a partir de 2017. El país se beneficia de una fuerza laboral altamente calificada y se encuentra entre los países más educados del mundo con uno de los porcentajes más altos de sus ciudadanos con un título de educación terciaria. Israel tiene el nivel de vida más alto de Oriente Medio y una de las esperanzas de vida más altas del mundo. |
|
| Description - |
1949 年,以色列(共和国)。 500 枚 Pruta“石榴弹”银币。铸币年份:1949 年参考编号:KM-16。发行量:33,812 枚面额:500 Pruta 状况:轻微接触痕迹和调色斑点,其他未流通!材质:银 (.500) 重量:24.95 克 直径:37 毫米 以色列(/ˈɪzriəl, -reɪəl/;希伯来语:ִׂשְׂרָאֵל;阿拉伯语:ץِْאֵَל),正式名称为以色列国,是中东的一个国家,位于地中海东南岸和红海北岸。它北部与黎巴嫩接壤,东北部与叙利亚接壤,东部与约旦接壤,东部和西部分别与约旦河西岸和加沙地带的巴勒斯坦领土接壤,西南与埃及接壤。该国在其相对较小的区域内具有多样化的地理特征。以色列的经济和技术中心是特拉维夫,而其政府所在地和宣布的首都是耶路撒冷,尽管该国对耶路撒冷的主权并未得到国际承认。以色列和犹大王国出现于铁器时代。新亚述帝国在公元前 720 年左右摧毁了以色列。犹大后来被巴比伦、波斯和希腊帝国征服,并作为犹太自治省份存在。成功的马卡比起义于公元前 110 年建立了一个独立的犹太王国,该王国于公元前 63 年结束,当时哈斯蒙尼王国成为罗马共和国的附庸国,随后于公元前 37 年建立了希律王朝,并于公元 6 年创建了罗马的犹太行省。犹太一直作为罗马行省存在,直到失败的犹太人起义导致大范围破坏、犹太人被驱逐以及该地区从犹太更名为叙利亚巴勒斯坦。 [28]几个世纪以来,犹太人在该地区的存在在一定程度上一直存在。 7 世纪,阿拉伯人从拜占庭帝国手中夺取黎凡特,并一直处于穆斯林控制之下,直到 1099 年第一次十字军东征,随后 1187 年阿尤布王朝征服。埃及马穆鲁克苏丹国在 13 世纪将其控制范围扩大到黎凡特直到 1517 年被奥斯曼帝国击败。 19 世纪期间,犹太人的民族觉醒导致犹太复国主义运动在散居海外的犹太人中兴起,随后出现了移民潮,移民到奥斯曼帝国,后来又移民到英属巴勒斯坦。 1947年,联合国通过了巴勒斯坦分治计划,建议建立独立的阿拉伯和犹太国家以及国际化的耶路撒冷。该计划被巴勒斯坦犹太机构接受,但遭到阿拉伯领导人的拒绝。次年,犹太机构宣布以色列国独立,随后的 1948 年阿拉伯-以色列战争中,以色列占领了大部分前托管领土,而约旦河西岸和加沙则由邻近的阿拉伯国家控制。此后,以色列与阿拉伯国家发生了多次战争,并自 1967 年以来占领了包括约旦河西岸、戈兰高地和加沙地带在内的领土(2005 年脱离接触后仍被视为被占领,尽管一些法律专家对这一说法提出异议)。它将其法律扩展到戈兰高地和东耶路撒冷,但没有扩展到西岸。以色列对巴勒斯坦领土的占领是近代世界上持续时间最长的军事占领。解决以色列-巴勒斯坦冲突的努力并未带来和平。然而,以色列与埃及和约旦之间已经签署了和平条约。在其《基本法》中,以色列将自己定义为犹太民主国家。以色列是代议制民主国家,实行议会制、比例代表制和普选权。总理是政府首脑,议会是立法机关。以色列是一个发达国家和经合组织成员国,截至 2017 年,按名义国内生产总值计算,以色列是世界第 33 大经济体。该国受益于高技能劳动力,是世界上受教育程度最高的国家之一,也是世界上受教育程度最高的国家之一。拥有高等教育学位的公民比例最高。以色列是中东地区生活水平最高的国家,也是世界上预期寿命最高的国家之一。 |


