| 5000 Reis Brasile Argento > Storia > Difference |
| Data revisione | 2019-04-22 00:16 (older) | 2024-04-02 18:28 (newer) |
| Postato da | ||
| Revision status | Verificata | Verificata |

|

|
|
| Denominazione | 5000 Reis | 5000 Reis |
| Stato | Brasile | Brasile |
| Periodo | 1938 | 1938 |
| Metallo | Argento | Argento |
| Persona | ||
| Categorie | ||
| Codice sul catalogo | KM 543 | KM 543 |
Descrizione -
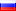 Русский
Русский
|
Бразилия 5000 рейс (1938 г.) Серебро Номер по Краузе KM#543, 600-я проба, 10 грамм, 26 мм. |
1938, Бразилия (Республика). Серебро 5000 рейсов «Пионер авиации Сантос-Дюмон» Год монетного двора: 1938 Артикул: КМ-543. Номинал: 5000 рейсов — бразильский изобретатель, пионер авиации Альберто Сантос-Дюмон. Материал: серебро (0,600). Вес: 10,11 г. Диаметр: 28 мм. просто Сантос-Дюмон) — бразильский изобретатель и пионер авиации, один из очень немногих людей, внесших значительный вклад в разработку самолетов как легче воздуха, так и тяжелее воздуха. Наследник богатой семьи производителей кофе, Сантос-Дюмон посвятил себя исследованиям и экспериментам в области авиации в Париже, где он провел большую часть своей взрослой жизни. В начале своей карьеры он проектировал, строил и управлял воздушными шарами и первыми дирижаблями, кульминацией чего стало получение 19 октября 1901 года премии Deutsch de la Meurthe за полет вокруг Эйфелевой башни. Затем он обратился к машинам тяжелее воздуха, и 23 октября 1906 года его 14-бис совершил первый в Европе полет на самолете тяжелее воздуха с двигателем, получивший сертификат Аэроклуба Франции и Международной авиационной федерации. Его убежденность в том, что авиация откроет эру всеобщего мира и процветания, побудила его свободно публиковать свои разработки и отказываться от патентования различных инноваций. Сантос-Дюмон – национальный герой Бразилии, где широко распространено мнение, что он опередил братьев Райт в демонстрации практичного самолета. Ему посвящены бесчисленные дороги, площади, школы, памятники и аэропорты, а его имя вписано в Пантеон Отечества и Свободы Танкредо Невес. Он был членом Бразильской академии литературы с 1931 года до своего самоубийства в 1932 году. Бразилия, официально Федеративная Республика Бразилия, является крупнейшим суверенным государством в Латинской Америке. Будучи федеративной республикой, Бразилия является пятой по величине страной в мире как по географической площади, так и по общей численности населения. Это крупнейшая португалоязычная страна в мире и единственная в Америке. Бразилия, ограниченная на востоке Атлантическим океаном, имеет береговую линию длиной 7491 км (4655 миль). Он граничит со всеми другими странами Южной Америки, кроме Эквадора и Чили, и занимает 47,3 процента континента Южной Америки. Бассейн реки Амазонки включает в себя обширные тропические леса, где обитает разнообразная дикая природа, разнообразные экологические системы и обширные природные ресурсы, охватывающие многочисленные охраняемые места обитания. Это уникальное экологическое наследие делает Бразилию одной из 17 стран с мегаразнообразием и является предметом значительного глобального интереса и дискуссий по вопросам вырубки лесов и защиты окружающей среды. Бразилия была населена многочисленными племенными народами до высадки в 1500 году исследователя Педру Альвареша Кабрала, который заявил права на эту территорию Португальской империи. Бразилия оставалась португальской колонией до 1808 года, когда столица империи была перенесена из Лиссабона в Рио-де-Жанейро. В 1815 году колония была возведена в ранг королевства после образования Соединенного Королевства Португалии, Бразилии и Алгарви. Независимость была достигнута в 1822 году с созданием Бразильской империи, унитарного государства, управляемого конституционной монархией и парламентской системой. Ратификация первой конституции в 1824 году привела к формированию двухпалатного законодательного органа, который теперь называется Национальным конгрессом. Страна стала президентской республикой в 1889 году после военного переворота. Авторитарная военная хунта пришла к власти в 1964 году и правила до 1985 года, после чего возобновилось гражданское управление. Действующая конституция Бразилии, сформулированная в 1988 году, определяет ее как федеративную республику. Федерация состоит из союза Федерального округа, 26 штатов и 5570 муниципалитетов. Бразилия имеет самое большое в мире население католиков и является самой густонаселенной страной в мире с католическим большинством. Экономика Бразилии является девятой в мире по номинальному ВВП и седьмой по величине ВВП (ППС) по состоянию на 2015 год. Будучи членом группы БРИКС, Бразилия до 2010 года имела одну из самых быстрорастущих крупных экономик мира, а ее экономические реформы давали стране новое международное признание и влияние. Национальный банк развития Бразилии играет важную роль в экономическом росте страны. Бразилия является одним из основателей Организации Объединенных Наций, «Большой двадцатки», БРИКС, Унасула, Меркосула, Организации американских государств, Организации иберо-американских государств, СПЯС и Латинского союза. Бразилия является региональной державой в Латинской Америке и средней державой в международных делах, причем некоторые аналитики называют ее развивающейся мировой державой. Бразилия, одна из крупнейших житниц мира, на протяжении последних 150 лет является крупнейшим производителем кофе. |
Descrizione -
 English
English
|
1938, Brazil (Republic). Silver 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Coin. XF- Mint Year: 1938 Reference: KM-543. Condition: A few edge-hits and scratches, otherwise a nice XF! Denominations: 5000 Reis - Brazilian inventor aviation pioneer Alberto Santos Dumont Material: Silver (.600) Weight: 10.11gm Diameter: 28mm Alberto Santos-Dumont (Portuguese: [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ]; 20 July 1873 – 23 July 1932, usually referred to as simply Santos-Dumont) was a Brazilian inventor and aviation pioneer, one of the very few people to have contributed significantly to the development of both lighter-than-air and heavier-than-air aircraft. The heir of a wealthy family of coffee producers, Santos-Dumont dedicated himself to aeronautical study and experimentation in Paris, where he spent most of his adult life. In his early career he designed, built, and flew hot air balloons and early dirigibles, culminating in his winning the Deutsch de la Meurthe prize on 19 October 1901 for a flight that rounded the Eiffel Tower. He then turned to heavier-than-air machines, and on 23 October 1906 his 14-bis made the first powered heavier-than-air flight in Europe to be certified by the Aéro-Club de France and the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. His conviction that aviation would usher in an era of worldwide peace and prosperity led him to freely publish his designs and forego patenting his various innovations. Santos-Dumont is a national hero in Brazil, where it is popularly held that he preceded the Wright brothers in demonstrating a practical airplane. Countless roads, plazas, schools, monuments, and airports there are dedicated to him, and his name is inscribed on the Tancredo Neves Pantheon of the Fatherland and Freedom. He was a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters from 1931 until his suicide in 1932.
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil is the largest sovereign state in Latin America. A federal republic, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country, by both geographical area and total population. It is the largest Portuguese-speaking country in the world, and the only one in the Americas. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of 7,491 km (4,655 mi). It borders all other South American countries except Ecuador and Chile and occupies 47.3 percent of the continent of South America. Its Amazon River basin includes a vast tropical forest, home to diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, and extensive natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats. This unique environmental heritage makes Brazil one of 17 megadiverse countries, and is the subject of significant global interest and debate regarding deforestation and environmental protection. Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d'état. An authoritarian military junta came to power in 1964 and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current constitution, formulated in 1988, defines it as a federal republic. The federation is composed of the union of the Federal District, the 26 states, and the 5,570 municipalities. Brazil has the world's highest population of Roman Catholics and is the world's most populous Catholic-majority country. Brazil's economy is the world's ninth-largest by nominal GDP and seventh-largest by GDP (PPP) as of 2015. A member of the BRICS group, Brazil until 2010 had one of the world's fastest growing major economies, with its economic reforms giving the country new international recognition and influence. Brazil's national development bank plays an important role for the country's economic growth. Brazil is a founding member of the United Nations, the G20, BRICS, Unasul, Mercosul, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States, CPLP and the Latin Union. Brazil is a regional power in Latin America and a middle power in international affairs, with some analysts identifying it as an emerging global power. One of the world's major breadbaskets, Brazil has been the largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years. Only 1$ shipping for each additional item purchased! |
1938, Brazil (Republic). Silver 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Mint Year: 1938 Reference: KM-543. Denominations: 5000 Reis - Brazilian inventor aviation pioneer Alberto Santos Dumont Material: Silver (.600) Weight: 10.11gm Diameter: 28mm Alberto Santos-Dumont (Portuguese: [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ]; 20 July 1873 – 23 July 1932, usually referred to as simply Santos-Dumont) was a Brazilian inventor and aviation pioneer, one of the very few people to have contributed significantly to the development of both lighter-than-air and heavier-than-air aircraft. The heir of a wealthy family of coffee producers, Santos-Dumont dedicated himself to aeronautical study and experimentation in Paris, where he spent most of his adult life. In his early career he designed, built, and flew hot air balloons and early dirigibles, culminating in his winning the Deutsch de la Meurthe prize on 19 October 1901 for a flight that rounded the Eiffel Tower. He then turned to heavier-than-air machines, and on 23 October 1906 his 14-bis made the first powered heavier-than-air flight in Europe to be certified by the Aéro-Club de France and the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. His conviction that aviation would usher in an era of worldwide peace and prosperity led him to freely publish his designs and forego patenting his various innovations. Santos-Dumont is a national hero in Brazil, where it is popularly held that he preceded the Wright brothers in demonstrating a practical airplane. Countless roads, plazas, schools, monuments, and airports there are dedicated to him, and his name is inscribed on the Tancredo Neves Pantheon of the Fatherland and Freedom. He was a member of the Brazilian Academy of Letters from 1931 until his suicide in 1932.
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil is the largest sovereign state in Latin America. A federal republic, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country, by both geographical area and total population. It is the largest Portuguese-speaking country in the world, and the only one in the Americas. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a coastline of 7,491 km (4,655 mi). It borders all other South American countries except Ecuador and Chile and occupies 47.3 percent of the continent of South America. Its Amazon River basin includes a vast tropical forest, home to diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, and extensive natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats. This unique environmental heritage makes Brazil one of 17 megadiverse countries, and is the subject of significant global interest and debate regarding deforestation and environmental protection. Brazil was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior to the landing in 1500 of explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral, who claimed the area for the Portuguese Empire. Brazil remained a Portuguese colony until 1808, when the capital of the empire was transferred from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. In 1815, the colony was elevated to the rank of kingdom upon the formation of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Independence was achieved in 1822 with the creation of the Empire of Brazil, a unitary state governed under a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary system. The ratification of the first constitution in 1824 led to the formation of a bicameral legislature, now called the National Congress. The country became a presidential republic in 1889 following a military coup d'état. An authoritarian military junta came to power in 1964 and ruled until 1985, after which civilian governance resumed. Brazil's current constitution, formulated in 1988, defines it as a federal republic. The federation is composed of the union of the Federal District, the 26 states, and the 5,570 municipalities. Brazil has the world's highest population of Roman Catholics and is the world's most populous Catholic-majority country. Brazil's economy is the world's ninth-largest by nominal GDP and seventh-largest by GDP (PPP) as of 2015. A member of the BRICS group, Brazil until 2010 had one of the world's fastest growing major economies, with its economic reforms giving the country new international recognition and influence. Brazil's national development bank plays an important role for the country's economic growth. Brazil is a founding member of the United Nations, the G20, BRICS, Unasul, Mercosul, Organization of American States, Organization of Ibero-American States, CPLP and the Latin Union. Brazil is a regional power in Latin America and a middle power in international affairs, with some analysts identifying it as an emerging global power. One of the world's major breadbaskets, Brazil has been the largest producer of coffee for the last 150 years. |
Descrizione -
 Deutsch
Deutsch
|
1938, Brasilien (Republik). Silber 5000 Reis „Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont“ Prägejahr: 1938 Referenz: KM-543. Nennwerte: 5000 Reis – Brasilianischer Erfinder, Luftfahrtpionier Alberto Santos Dumont. Material: Silber (.600). Gewicht: 10,11 g einfach Santos-Dumont genannt) war ein brasilianischer Erfinder und Luftfahrtpionier und einer der ganz wenigen Menschen, die maßgeblich zur Entwicklung sowohl von Flugzeugen, die leichter als Luft als auch schwerer als Luft waren, beigetragen haben. Als Erbe einer wohlhabenden Familie von Kaffeeproduzenten widmete sich Santos-Dumont Luftfahrtstudien und Experimenten in Paris, wo er den größten Teil seines Erwachsenenlebens verbrachte. In seiner frühen Karriere entwarf, baute und flog er Heißluftballons und frühe Luftschiffe, was seinen Höhepunkt darin fand, dass er am 19. Oktober 1901 den Deutsch-de-la-Meurthe-Preis für einen Flug um den Eiffelturm gewann. Anschließend wandte er sich Maschinen zu, die schwerer als Luft sind, und am 23. Oktober 1906 unternahm seine 14-bis den ersten motorisierten Flug, der schwerer als Luft war, in Europa, der vom Aéro-Club de France und der Fédération Aéronautique Internationale zertifiziert wurde. Seine Überzeugung, dass die Luftfahrt eine Ära des weltweiten Friedens und Wohlstands einläuten würde, veranlasste ihn, seine Entwürfe frei zu veröffentlichen und auf die Patentierung seiner verschiedenen Innovationen zu verzichten. Santos-Dumont ist ein Nationalheld in Brasilien, wo allgemein angenommen wird, dass er den Gebrüdern Wright bei der Demonstration eines praktischen Flugzeugs voraus war. Unzählige Straßen, Plätze, Schulen, Denkmäler und Flughäfen sind ihm gewidmet, und sein Name ist in das Pantheon des Vaterlandes und der Freiheit von Tancredo Neves eingraviert. Von 1931 bis zu seinem Selbstmord im Jahr 1932 war er Mitglied der Brasilianischen Akademie der Literatur. Brasilien, offiziell die Föderative Republik Brasilien, ist der größte souveräne Staat Lateinamerikas. Als Bundesrepublik ist Brasilien sowohl nach geografischer Fläche als auch nach Gesamtbevölkerung das fünftgrößte Land der Welt. Es ist das größte portugiesischsprachige Land der Welt und das einzige auf dem amerikanischen Kontinent. Brasilien wird im Osten vom Atlantischen Ozean begrenzt und hat eine Küstenlinie von 7.491 km (4.655 Meilen). Es grenzt an alle anderen südamerikanischen Länder außer Ecuador und Chile und nimmt 47,3 Prozent des südamerikanischen Kontinents ein. Das Einzugsgebiet des Amazonas umfasst einen ausgedehnten tropischen Wald, der eine vielfältige Tierwelt, eine Vielzahl von Ökosystemen und umfangreiche natürliche Ressourcen beherbergt, die zahlreiche geschützte Lebensräume umfassen. Dieses einzigartige Umwelterbe macht Brasilien zu einem von 17 Ländern mit großer Vielfalt und ist Gegenstand erheblichen globalen Interesses und einer Debatte über Entwaldung und Umweltschutz. Vor der Landung des Entdeckers Pedro Álvares Cabral im Jahr 1500, der das Gebiet für das portugiesische Reich beanspruchte, wurde Brasilien von zahlreichen Stammesnationen bewohnt. Brasilien blieb bis 1808 eine portugiesische Kolonie, als die Hauptstadt des Reiches von Lissabon nach Rio de Janeiro verlegt wurde. Im Jahr 1815 wurde die Kolonie mit der Gründung des Vereinigten Königreichs Portugal, Brasilien und den Algarven in den Rang eines Königreichs erhoben. Die Unabhängigkeit wurde 1822 mit der Gründung des brasilianischen Imperiums erreicht, einem Einheitsstaat, der von einer konstitutionellen Monarchie und einem parlamentarischen System regiert wird. Die Ratifizierung der ersten Verfassung im Jahr 1824 führte zur Bildung einer Zweikammer-Legislative, die heute Nationalkongress genannt wird. Das Land wurde 1889 nach einem Militärputsch eine Präsidialrepublik. Eine autoritäre Militärjunta kam 1964 an die Macht und regierte bis 1985, danach wurde die zivile Regierung wieder aufgenommen. Die aktuelle Verfassung Brasiliens aus dem Jahr 1988 definiert das Land als föderale Republik. Der Bund besteht aus dem Bundesdistrikt, den 26 Bundesstaaten und den 5.570 Gemeinden. Brasilien hat die höchste römisch-katholische Bevölkerung der Welt und ist das bevölkerungsreichste Land der Welt mit katholischer Mehrheit. Brasiliens Wirtschaft ist gemessen am nominalen BIP die neuntgrößte der Welt und gemessen am BIP (KKP) die siebtgrößte (Stand 2015). Als Mitglied der BRICS-Gruppe hatte Brasilien bis 2010 mit seinen Wirtschaftsreformen eine der am schnellsten wachsenden großen Volkswirtschaften der Welt Land neue internationale Anerkennung und Einfluss. Die nationale Entwicklungsbank Brasiliens spielt eine wichtige Rolle für das Wirtschaftswachstum des Landes. Brasilien ist Gründungsmitglied der Vereinten Nationen, der G20, der BRICS, der Unasul, des Mercosul, der Organisation Amerikanischer Staaten, der Organisation Iberoamerikanischer Staaten, der CPLP und der Lateinischen Union. Brasilien ist eine Regionalmacht in Lateinamerika und eine Mittelmacht in internationalen Angelegenheiten, wobei einige Analysten es als eine aufstrebende Weltmacht bezeichnen. Brasilien ist einer der größten Kornkammern der Welt und seit 150 Jahren der größte Kaffeeproduzent. |
|
Descrizione -
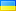 Українська
Українська
|
1938, Бразилія (республіка). Срібло 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Рік монетного двору: 1938 Реєстрація: KM-543. Номінали: 5000 рейсів – бразильський винахідник, піонер авіації Альберто Сантос Дюмон Матеріал: срібло (.600) Вага: 10,11 г Діаметр: 28 мм Альберто Сантос-Дюмон (португальська: [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ]; 20 липня 1873 – 23 липня 1932, зазвичай згадується до як просто Сантос-Дюмон) був бразильським винахідником і піонером авіації, одним із небагатьох людей, які зробили значний внесок у розробку літальних апаратів як легших за повітря, так і важчих за повітря. Спадкоємець багатої родини виробників кави, Сантос-Дюмон присвятив себе аеронавігації та експериментам у Парижі, де він провів більшу частину свого дорослого життя. На початку своєї кар’єри він проектував, будував і літав на повітряних кулях і ранніх дирижаблях, кульмінацією якої став виграш премії Deutsch de la Meurthe 19 жовтня 1901 року за політ навколо Ейфелевої вежі. Потім він звернувся до апаратів, важчих за повітря, і 23 жовтня 1906 року його 14-біс здійснив перший політ на двигуні важчий за повітря в Європі, який був сертифікований Aéro-Club de France і Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. Його переконання в тому, що авіація започаткує еру всесвітнього миру та процвітання, спонукало його вільно публікувати свої проекти та відмовитися від патентування різноманітних інновацій. Сантос-Дюмон є національним героєм Бразилії, де прийнято вважати, що він випередив братів Райт у демонстрації практичного літака. Йому присвячено незліченну кількість доріг, площ, шкіл, пам’ятників і аеропортів, а його ім’я вписано в Пантеон Вітчизни та Свободи Танкредо Невеса. Він був членом Бразильської академії літератури з 1931 року до свого самогубства в 1932 році. Бразилія, офіційна назва Федеративна Республіка Бразилія, є найбільшою суверенною державою в Латинській Америці. Федеративна республіка, Бразилія є п’ятою за величиною країною світу як за географічною площею, так і за загальною кількістю населення. Це найбільша португаломовна країна у світі та єдина на американському континенті. Бразилія, омивається Атлантичним океаном на сході, має берегову лінію протяжністю 7491 км (4655 миль). Вона межує з усіма іншими південноамериканськими країнами, крім Еквадору та Чилі, і займає 47,3 відсотка континенту Південна Америка. Басейн річки Амазонка включає величезний тропічний ліс, де мешкає різноманітна дика природа, різноманітні екологічні системи та великі природні ресурси, що охоплюють численні охоронювані середовища проживання. Ця унікальна екологічна спадщина робить Бразилію однією з 17 країн із величезним різноманіттям і є предметом значного глобального інтересу та дискусій щодо вирубки лісів та захисту навколишнього середовища. Бразилія була населена численними племінними націями до висадки в 1500 році дослідника Педру Алвареса Кабрала, який заявив, що ця територія належить Португальській імперії. Бразилія залишалася португальською колонією до 1808 року, коли столицю імперії було перенесено з Лісабона до Ріо-де-Жанейро. У 1815 році колонія була піднесена до рангу королівства після утворення Сполученого Королівства Португалії, Бразилії та Алгарвів. Незалежність була досягнута в 1822 році зі створенням Бразильської імперії, унітарної держави, керованої конституційною монархією та парламентською системою. Ратифікація першої конституції в 1824 році призвела до формування двопалатного законодавчого органу, який тепер називається Національним конгресом. Країна стала президентською республікою в 1889 році після військового перевороту. Авторитарна військова хунта прийшла до влади в 1964 році і правила до 1985 року, після чого відновилося цивільне управління. Чинна конституція Бразилії, сформульована в 1988 році, визначає її як федеративну республіку. Федерація складається з федерального округу, 26 штатів і 5570 муніципалітетів. Бразилія має найбільшу кількість римо-католиків у світі та є найбільшою у світі країною з католицькою більшістю. Економіка Бразилії є дев’ятою за розміром номінального ВВП і сьомою за розміром ВВП (ПКС) станом на 2015 рік. Член групи БРІКС, Бразилія до 2010 року мала одну з найбільш швидкозростаючих великих економік у світі, а її економічні реформи дали нове міжнародне визнання та вплив країни. Національний банк розвитку Бразилії відіграє важливу роль в економічному зростанні країни. Бразилія є членом-засновником ООН, G20, БРІКС, Унасул, Меркосул, Організації американських держав, Організації іберо-американських держав, CPLP і Латинського союзу. Бразилія є регіональною державою в Латинській Америці та середньою силою в міжнародних справах, а деякі аналітики вважають її новою глобальною державою. Одна з найбільших світових житниць, Бразилія була найбільшим виробником кави протягом останніх 150 років. |
|
Descrizione -
 Italiano
Italiano
|
1938, Brasile (Repubblica). Argento 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Anno di zecca: 1938 Riferimento: KM-543. Denominazioni: 5000 Reis - Inventore brasiliano, pioniere dell'aviazione Alberto Santos Dumont Materiale: Argento (.600) Peso: 10,11 g Diametro: 28 mm Alberto Santos-Dumont (portoghese: [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ]; 20 luglio 1873 – 23 luglio 1932, solitamente indicato come come semplicemente Santos-Dumont) è stato un inventore brasiliano e pioniere dell'aviazione, una delle pochissime persone ad aver contribuito in modo significativo allo sviluppo di velivoli sia più leggeri che più pesanti dell'aria. Erede di una ricca famiglia di produttori di caffè, Santos-Dumont si dedicò agli studi e alla sperimentazione aeronautica a Parigi, dove trascorse gran parte della sua vita adulta. All'inizio della sua carriera progettò, costruì e volò mongolfiere e primi dirigibili, culminando con la vittoria del premio Deutsch de la Meurthe il 19 ottobre 1901 per un volo che doppiava la Torre Eiffel. Si dedicò quindi a macchine più pesanti dell'aria e il 23 ottobre 1906 il suo 14-bis effettuò il primo volo a motore più pesante dell'aria in Europa ad essere certificato dall'Aéro-Club de France e dalla Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. La sua convinzione che l'aviazione avrebbe inaugurato un'era di pace e prosperità mondiale lo portò a pubblicare liberamente i suoi progetti e a rinunciare a brevettare le sue varie innovazioni. Santos-Dumont è un eroe nazionale in Brasile, dove si ritiene comunemente che abbia preceduto i fratelli Wright nella dimostrazione di un aereo pratico. A lui sono dedicate innumerevoli strade, piazze, scuole, monumenti e aeroporti e il suo nome è iscritto nel Pantheon della Patria e della Libertà di Tancredo Neves. Fu membro dell'Accademia brasiliana di lettere dal 1931 fino al suo suicidio nel 1932. Il Brasile, ufficialmente Repubblica Federativa del Brasile, è il più grande stato sovrano dell'America Latina. Repubblica federale, il Brasile è il quinto paese più grande del mondo, sia per area geografica che per popolazione totale. È il paese di lingua portoghese più grande del mondo e l'unico delle Americhe. Delimitato dall'Oceano Atlantico a est, il Brasile ha una costa di 7.491 km (4.655 mi). Confina con tutti gli altri paesi sudamericani tranne l'Ecuador e il Cile e occupa il 47,3% del continente sudamericano. Il bacino del Rio delle Amazzoni comprende una vasta foresta tropicale, che ospita diversi animali selvatici, una varietà di sistemi ecologici e vaste risorse naturali che abbracciano numerosi habitat protetti. Questo patrimonio ambientale unico rende il Brasile uno dei 17 paesi del megadiverso ed è oggetto di un significativo interesse e dibattito globale riguardo alla deforestazione e alla protezione ambientale. Il Brasile era abitato da numerose nazioni tribali prima dello sbarco nel 1500 dell'esploratore Pedro Álvares Cabral, che rivendicò l'area per l'Impero portoghese. Il Brasile rimase una colonia portoghese fino al 1808, quando la capitale dell'impero fu trasferita da Lisbona a Rio de Janeiro. Nel 1815, la colonia fu elevata al rango di regno dopo la formazione del Regno Unito di Portogallo, Brasile e Algarves. L'indipendenza fu raggiunta nel 1822 con la creazione dell'Impero del Brasile, uno stato unitario governato da una monarchia costituzionale e da un sistema parlamentare. La ratifica della prima costituzione nel 1824 portò alla formazione di una legislatura bicamerale, ora chiamata Congresso Nazionale. Il paese divenne una repubblica presidenziale nel 1889 a seguito di un colpo di stato militare. Una giunta militare autoritaria salì al potere nel 1964 e governò fino al 1985, dopodiché riprese il governo civile. L'attuale costituzione del Brasile, formulata nel 1988, lo definisce una repubblica federale. La federazione è composta dall'unione del Distretto Federale, dei 26 stati e dei 5.570 comuni. Il Brasile ha la più alta popolazione mondiale di cattolici romani ed è il paese a maggioranza cattolica più popoloso al mondo. L'economia del Brasile è la nona più grande al mondo per PIL nominale e la settima per PIL (PPA) nel 2015. Membro del gruppo BRICS, il Brasile fino al 2010 aveva una delle principali economie in più rapida crescita al mondo, con le sue riforme economiche che davano il paese nuovo riconoscimento e influenza internazionale. La Banca nazionale di sviluppo del Brasile svolge un ruolo importante per la crescita economica del Paese. Il Brasile è un membro fondatore delle Nazioni Unite, del G20, dei BRICS, dell'Unasul, del Mercosul, dell'Organizzazione degli Stati Americani, dell'Organizzazione degli Stati Iberoamericani, del CPLP e dell'Unione Latina. Il Brasile è una potenza regionale in America Latina e una potenza media negli affari internazionali, con alcuni analisti che lo identificano come una potenza globale emergente. Uno dei maggiori granai del mondo, il Brasile è stato il più grande produttore di caffè negli ultimi 150 anni. |
|
Descrizione -
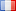 Français
Français
|
1938, Brésil (République). Argent 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Mint Année : 1938 Référence : KM-543. Valeurs nominales : 5000 Reis - Inventeur brésilien, pionnier de l'aviation, Alberto Santos Dumont Matériau : Argent (.600) Poids : 10,11 g Diamètre : 28 mm Alberto Santos-Dumont (portugais : [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ] ; 20 juillet 1873 – 23 juillet 1932, généralement appelé comme simplement Santos-Dumont) était un inventeur brésilien et un pionnier de l'aviation, l'une des rares personnes à avoir contribué de manière significative au développement d'avions à la fois plus légers et plus lourds que l'air. Héritier d'une riche famille de producteurs de café, Santos-Dumont se consacre aux études et à l'expérimentation aéronautiques à Paris, où il passe la majeure partie de sa vie d'adulte. Au début de sa carrière, il a conçu, construit et piloté des montgolfières et des premiers dirigeables, ce qui lui a valu de remporter le prix Deutsch de la Meurthe le 19 octobre 1901 pour un vol contournant la Tour Eiffel. Il se tourne alors vers les engins plus lourds que l'air et, le 23 octobre 1906, son 14-bis effectue le premier vol propulsé plus lourd que l'air en Europe à être certifié par l'Aéro-Club de France et la Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. Sa conviction que l’aviation inaugurerait une ère de paix et de prospérité mondiales l’a amené à publier librement ses créations et à renoncer à breveter ses diverses innovations. Santos-Dumont est un héros national au Brésil, où l'on considère généralement qu'il a précédé les frères Wright dans la démonstration d'un avion pratique. D'innombrables routes, places, écoles, monuments et aéroports lui sont dédiés, et son nom est inscrit sur le Panthéon Tancredo Neves de la Patrie et de la Liberté. Il fut membre de l'Académie brésilienne des lettres de 1931 jusqu'à son suicide en 1932. Le Brésil, officiellement la République fédérative du Brésil, est le plus grand État souverain d'Amérique latine. République fédérale, le Brésil est le cinquième plus grand pays du monde, tant par sa superficie géographique que par sa population totale. C’est le plus grand pays lusophone au monde et le seul des Amériques. Bordé par l'océan Atlantique à l'est, le Brésil possède un littoral de 7 491 km (4 655 mi). Il borde tous les autres pays d'Amérique du Sud, à l'exception de l'Équateur et du Chili, et occupe 47,3 pour cent du continent sud-américain. Son bassin fluvial amazonien comprend une vaste forêt tropicale, abritant une faune diversifiée, une variété de systèmes écologiques et de vastes ressources naturelles couvrant de nombreux habitats protégés. Ce patrimoine environnemental unique fait du Brésil l'un des 17 pays mégadivers et fait l'objet d'un intérêt et d'un débat mondiaux importants concernant la déforestation et la protection de l'environnement. Le Brésil était habité par de nombreuses nations tribales avant le débarquement en 1500 de l'explorateur Pedro Álvares Cabral, qui revendique la région pour le compte de l'Empire portugais. Le Brésil resta une colonie portugaise jusqu'en 1808, date à laquelle la capitale de l'empire fut transférée de Lisbonne à Rio de Janeiro. En 1815, la colonie fut élevée au rang de royaume lors de la formation du Royaume-Uni du Portugal, du Brésil et des Algarves. L'indépendance a été obtenue en 1822 avec la création de l'Empire du Brésil, un État unitaire gouverné par une monarchie constitutionnelle et un système parlementaire. La ratification de la première constitution en 1824 a conduit à la formation d'une législature bicamérale, aujourd'hui appelée Congrès national. Le pays est devenu une république présidentielle en 1889 à la suite d'un coup d'État militaire. Une junte militaire autoritaire est arrivée au pouvoir en 1964 et a régné jusqu’en 1985, après quoi la gouvernance civile a repris. La constitution actuelle du Brésil, formulée en 1988, le définit comme une république fédérale. La fédération est composée de l'union du District fédéral, des 26 États et des 5 570 communes. Le Brésil a la plus grande population de catholiques romains au monde et est le pays à majorité catholique le plus peuplé du monde. L'économie du Brésil est la neuvième au monde en termes de PIB nominal et la septième en termes de PIB (PPA) en 2015. Membre du groupe BRICS, le Brésil avait jusqu'en 2010 l'une des principales économies à la croissance la plus rapide au monde, avec ses réformes économiques donnant le pays nouvelle reconnaissance et influence internationale. La banque nationale de développement du Brésil joue un rôle important dans la croissance économique du pays. Le Brésil est membre fondateur des Nations Unies, du G20, des BRICS, de l'Unasul, du Mercosul, de l'Organisation des États américains, de l'Organisation des États ibéro-américains, de la CPLP et de l'Union latine. Le Brésil est une puissance régionale en Amérique latine et une puissance moyenne dans les affaires internationales, certains analystes l’identifiant comme une puissance mondiale émergente. L'un des principaux greniers à blé du monde, le Brésil est le plus grand producteur de café depuis 150 ans. |
|
Descrizione -
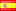 Español
Español
|
1938, Brasil (República). Plata 5000 Reis "Aviation Pioneer Santos-Dumont" Año de Ceca: 1938 Referencia: KM-543. Denominaciones: 5000 Reis - Inventor brasileño pionero de la aviación Alberto Santos Dumont Material: Plata (.600) Peso: 10,11 g Diámetro: 28 mm Alberto Santos-Dumont (portugués: [awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ]; 20 de julio de 1873 - 23 de julio de 1932, generalmente mencionado como simplemente Santos-Dumont) fue un inventor y pionero de la aviación brasileño, una de las pocas personas que contribuyó significativamente al desarrollo de aviones tanto más ligeros como más pesados que el aire. Heredero de una adinerada familia de productores de café, Santos-Dumont se dedicó al estudio y la experimentación aeronáutica en París, donde pasó la mayor parte de su vida adulta. Al principio de su carrera diseñó, construyó y voló globos aerostáticos y los primeros dirigibles, que culminaron con la obtención del premio Deutsch de la Meurthe el 19 de octubre de 1901 por un vuelo que rodeó la Torre Eiffel. Luego recurrió a máquinas más pesadas que el aire y, el 23 de octubre de 1906, su 14-bis realizó el primer vuelo con motor más pesado que el aire en Europa certificado por el Aéro-Club de France y la Fédération Aéronautique Internationale. Su convicción de que la aviación marcaría el comienzo de una era de paz y prosperidad mundial lo llevó a publicar libremente sus diseños y a renunciar a patentar sus diversas innovaciones. Santos-Dumont es un héroe nacional en Brasil, donde se cree popularmente que precedió a los hermanos Wright en la demostración de un avión práctico. A él están dedicados innumerables caminos, plazas, escuelas, monumentos y aeropuertos, y su nombre está inscrito en el Panteón de la Patria y la Libertad Tancredo Neves. Fue miembro de la Academia Brasileña de Letras desde 1931 hasta su suicidio en 1932. Brasil, oficialmente República Federativa de Brasil, es el estado soberano más grande de América Latina. Brasil, una república federal, es el quinto país más grande del mundo, tanto por área geográfica como por población total. Es el país de habla portuguesa más grande del mundo y el único de América. Limitado por el Océano Atlántico al este, Brasil tiene una costa de 7.491 km (4.655 millas). Limita con todos los demás países de América del Sur excepto Ecuador y Chile y ocupa el 47,3 por ciento del continente de América del Sur. La cuenca del río Amazonas incluye un vasto bosque tropical, hogar de diversa vida silvestre, una variedad de sistemas ecológicos y extensos recursos naturales que abarcan numerosos hábitats protegidos. Este patrimonio ambiental único convierte a Brasil en uno de los 17 países megadiversos y es objeto de importante interés y debate global sobre la deforestación y la protección ambiental. Brasil estaba habitado por numerosas naciones tribales antes del desembarco en 1500 del explorador Pedro Álvares Cabral, quien reclamó el área para el Imperio portugués. Brasil siguió siendo colonia portuguesa hasta 1808, cuando la capital del imperio fue trasladada de Lisboa a Río de Janeiro. En 1815, la colonia fue elevada al rango de reino tras la formación del Reino Unido de Portugal, Brasil y Algarves. La independencia se logró en 1822 con la creación del Imperio de Brasil, un estado unitario gobernado bajo una monarquía constitucional y un sistema parlamentario. La ratificación de la primera constitución en 1824 condujo a la formación de una legislatura bicameral, ahora llamada Congreso Nacional. El país se convirtió en una república presidencial en 1889 tras un golpe de estado militar. Una junta militar autoritaria llegó al poder en 1964 y gobernó hasta 1985, después de lo cual se reanudó el gobierno civil. La actual constitución de Brasil, formulada en 1988, lo define como una república federal. La federación está compuesta por la unión del Distrito Federal, los 26 estados y los 5,570 municipios. Brasil tiene la mayor población de católicos romanos del mundo y es el país de mayoría católica más poblado del mundo. La economía de Brasil es la novena más grande del mundo por PIB nominal y la séptima por PIB (PPA) en 2015. Brasil, miembro del grupo BRICS, hasta 2010 tenía una de las principales economías de más rápido crecimiento del mundo, y sus reformas económicas le dieron la país nuevo reconocimiento e influencia internacional. El banco nacional de desarrollo de Brasil desempeña un papel importante para el crecimiento económico del país. Brasil es miembro fundador de las Naciones Unidas, el G20, los BRICS, la Unasul, el Mercosur, la Organización de Estados Americanos, la Organización de Estados Iberoamericanos, la CPLP y la Unión Latina. Brasil es una potencia regional en América Latina y una potencia intermedia en los asuntos internacionales, y algunos analistas lo identifican como una potencia global emergente. Brasil, uno de los principales graneros del mundo, ha sido el mayor productor de café durante los últimos 150 años. |
|
| Descrizione - |
1938 年,巴西(共和国)。银质 5000 Reis“航空先锋桑托斯-杜蒙”铸币年份:1938 参考号:KM-543。面额:5000雷斯 - 巴西发明家航空先驱Alberto Santos Dumont 材质:银(.600) 重量:10.11gm 直径:28mm Alberto Santos-Dumont(葡萄牙语:[awˈbɛʁtu ˈsɐ̃tuz duˈmõ];1873年7月20日 - 1932年7月23日,通常简称桑托斯-杜蒙(Santos-Dumont)是巴西发明家和航空先驱,是为轻于空气和重于空气飞机的发展做出重大贡献的极少数人之一。桑托斯·杜蒙是一个富裕的咖啡生产商家族的继承人,他在巴黎致力于航空研究和实验,并在那里度过了他成年后的大部分时间。在他的早期职业生涯中,他设计、建造并驾驶了热气球和早期飞船,最终于 1901 年 10 月 19 日凭借绕埃菲尔铁塔的飞行赢得了 Deutsch de la Meurthe 奖。然后,他转向重于空气的机器,并于 1906 年 10 月 23 日,他的 14-bis 进行了欧洲首次动力重于空气的飞行,并获得了法国航空俱乐部和国际航空联合会的认证。他坚信航空业将迎来一个世界和平与繁荣的时代,这促使他自由地发布他的设计并放弃为他的各种创新申请专利。桑托斯-杜蒙是巴西的民族英雄,人们普遍认为他先于莱特兄弟展示了一架实用的飞机。那里有无数的道路、广场、学校、纪念碑和机场都是为了纪念他而修建的,他的名字也被刻在坦克雷多·内维斯祖国与自由万神殿上。从 1931 年到 1932 年自杀为止,他一直是巴西文学学院的成员。巴西,正式名称为巴西联邦共和国,是拉丁美洲最大的主权国家。巴西是一个联邦共和国,按地理面积和总人口计算,是世界第五大国家。它是世界上最大的葡语国家,也是美洲唯一的葡语国家。巴西东临大西洋,海岸线长 7,491 公里(4,655 英里)。它与除厄瓜多尔和智利外的所有其他南美洲国家接壤,占南美洲大陆面积的47.3%。亚马逊河流域拥有广阔的热带森林,是多种野生动物、多种生态系统以及遍布众多受保护栖息地的丰富自然资源的家园。这种独特的环境遗产使巴西成为 17 个生物多样性大国之一,并且成为全球关于森林砍伐和环境保护的重大兴趣和辩论的主题。 1500 年,探险家佩德罗·阿尔瓦雷斯·卡布拉尔 (Pedro Álvares Cabral) 登陆巴西,葡萄牙帝国宣称拥有该地区。在此之前,巴西曾居住着众多部落民族。巴西一直是葡萄牙殖民地,直到 1808 年帝国首都从里斯本迁至里约热内卢。 1815年,葡萄牙、巴西和阿尔加维联合王国成立,该殖民地晋升为王国。 1822 年巴西帝国成立,实现独立,这是一个实行君主立宪制和议会制的单一国家。 1824 年第一部宪法的批准导致了两院制立法机构的成立,即现在的国民议会。 1889 年军事政变后,该国成为总统共和制国家。 1964年,独裁军政府上台并统治至1985年,此后恢复文官治理。巴西现行宪法于1988年制定,将其定义为联邦共和国。该联邦由联邦区、26 个州和 5,570 个市的联盟组成。巴西是世界上罗马天主教徒人口最多的国家,也是世界上天主教人口最多的国家。截至 2015 年,巴西经济按名义 GDP 排名世界第九,按 GDP(购买力平价)排名第七。作为金砖国家集团成员,巴西在 2010 年之前一直是世界上增长最快的主要经济体之一,其经济改革使国家新的国际认可度和影响力。巴西国家开发银行对该国经济增长发挥着重要作用。巴西是联合国、二十国集团、金砖国家、南美共同市场、南方共同市场、美洲国家组织、伊比利亚美洲国家组织、葡语国家共同体和拉丁联盟的创始成员。巴西是拉丁美洲的地区大国,也是国际事务中的中等强国,一些分析人士将其视为新兴的全球大国。巴西是世界主要粮仓之一,在过去 150 年里一直是最大的咖啡生产国。 |


