1 Rubel (Verkauft für $132.0)
1893, Russia, Emperor Alexander III. Silver Rouble Coin. (BV:$600 in VF!) Rare!
Mint Year: 1893 Denomination: 1 Rouble Mint Place: St. Petersburg Mint Master: Appolon Grasgov (AG) Reference: Davenport 292, KM-46 ($600 in VF!). R! Condition: Scratches and deposits, edge-hits, otherwise a nice VF+ Material: Gold (.900) Weight: 19.74gm Diameter: 33mm
Obverse: Bearded head on Alexander III right. Legend (translated): "Alexander III Emperor and Sole Ruler of all Russians *" Reverse:Heraldic eagle with shields of provinces (duchies), holding imperial orb and staff. Legend (translated): "Robule 1893 Year"
Alexander III Alexandrovich (10 March [O.S. 26 February] 1845 – 1 November [O.S. 20 October] 1894) (Aleksandr III Aleksandrovich) reigned as Emperor of Russia from 13 March 1881 until his death in 1894. Unlike his assassinated father, liberal-leaning Alexander II, Alexander III is considered by historians to have been a repressive and reactionary tsar.
Alexander III was born in Saint Petersburg, the second son of Czar Alexander II by his wife Princess Marie of Hesse and by Rhine.
In disposition, he bore little resemblance to his soft-hearted, liberal father, and still less to his refined, philosophic, sentimental, chivalrous, yet cunning granduncle Alexander I, who coveted the title of "the first gentleman of Europe".
Although an enthusiastic amateur musician and patron of the ballet, he was seen as lacking refinement and elegance. Indeed, he rather relished the idea of being of the same rough texture as the great majority of his subjects.
His straightforward, abrupt manner savoured sometimes of gruffness, while his direct, unadorned method of expressing himself harmonized well with his rough-hewn, immobile features and somewhat sluggish movements. His education was not such as to soften these peculiarities.
He was also noted for his immense physical strength, though the large boil on the left side of his nose caused him to be severely mocked by his contemporaries, hence why he always sat for photographs and portraits with the right side of his face most prominent.
During the first twenty years of his life, Alexander had little prospect of succeeding to the throne, because he had an elder brother, Nicholas, who seemed of robust constitution.
Even when this elder brother first showed symptoms of delicate health, the notion that he might die young was never seriously taken; Nicholas was betrothed to the Princess Dagmar of Denmark.
Under these circumstances, the greatest solicitude was devoted to the education of Nicholas as Tsarevich, whereas Alexander received only the perfunctory and inadequate training of an ordinary Grand Duke of that period, which did not go much beyond secondary instruction, with practical acquaintance in French, English and German, and a certain amount of military drill.
Alexander became heir apparent by the sudden death of his elder brother in 1865.
It was then that he began to study the principles of law and administration under Konstantin Pobedonostsev, who was then a professor of civil law at Moscow State University and who later (in 1880) became chief procurator of the Holy Synod.
Pobedonostsev awakened in his pupil very little love for abstract studies or prolonged intellectual exertion, but he influenced the character of Alexander's reign by instilling into the young man's mind the belief that zeal for Russian Orthodox thought was an essential factor of Russian patriotism and that this was to be specially cultivated by every right-minded Tsar.
On his deathbed, Alexander's elder brother Nicholas is said to have expressed the wish that his affianced bride, Princess Dagmar of Denmark, should marry his successor.
This wish was swiftly realized, when on 9 November [O.S. 28 October] 1866 in the Imperial Chapel of the Winter Palace in St. Petersburg, Alexander wed the Princess of Denmark.
The union proved a most happy one and remained unclouded to the end. Unlike that of his parents, there was no adultery in the marriage.
During those years when he was heir-apparent—1865 to 1881—Alexander did not play a prominent part in public affairs, but he allowed it to become known that he had certain ideas of his own which did not coincide with the principles of the existing government.
Alexander deprecated what he considered undue foreign influence in general, and German influence in particular, so the adoption of genuine national principles was off in all spheres of official activity, with a view to realizing his ideal of a homogeneous Russia—homogeneous in language, administration and religion. With such ideas and aspirations he could hardly remain permanently in cordial agreement with his father, who, though a good patriot according to his lights, had strong German sympathies, often used the German language in his private relations, occasionally ridiculed the exaggerations and eccentricities of the Slavophiles and based his foreign policy on the Prussian alliance.
The antagonism first appeared publicly during the Franco-Prussian War, when the Tsar supported the cabinet of Berlin and the Tsarevich did not conceal his sympathies for the French. It reappeared in an intermittent fashion during the years 1875–1879, when the Eastern question produced so much excitement in all ranks of Russian Society. At first the Tsarevich was more Slavophile than the government, but his phlegmatic nature preserved him from many of the exaggerations indulged in by others, and any of the prevalent popular illusions he may have imbibed were soon dispelled by personal observation in Bulgaria, where he commanded the left wing of the invading army.
Never consulted on political questions, he confined himself to his military duties and fulfilled them in a conscientious and unobtrusive manner. After many mistakes and disappointments, the army reached Constantinople and the Treaty of San Stefano was signed, but much that had been obtained by that important document had to be sacrificed at the Congress of Berlin. Bismarck failed to do what was confidently expected of him by the Russian Tsar.
In return for the Russian support, which had enabled him to create the German Empire, it was thought that he would help Russia to solve the Eastern question in accordance with her own interests, but to the surprise and indignation of the cabinet of Saint Petersburg he confined himself to acting the part of "honest broker" at the Congress, and shortly afterwards he ostentatiously contracted an alliance with Austria for the express purpose of counteracting Russian designs in Eastern Europe. The Tsarevich could point to these results as confirming the views he had expressed during the Franco-Prussian War, and he drew from them the practical conclusion that for Russia the best thing to do was to recover as quickly as possible from her temporary exhaustion and to prepare for future contingencies by a radical scheme of military and naval reorganization. In accordance with this conviction, he suggested that certain reforms should be introduced.
Only 1$ shipping for each additional item purchased!

serega » Рубли (16 Münzen)
Рубли Российской Империи со времен Петра Великого до Николая II. Серебро. Просто красивые рубчики :)

|
Beigetragen von:
anonymous 2021-03-17 |
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
1 Rupee Britisches Weltreich (1497 - 1949) Silber
Diese Gruppe hat 11 Münzen / 10 Preise
⇑

-600-300-8TzGdOsxqQEAAAF4t5hGgj7K.jpg)

-300-150-pTAKbzbihgwAAAFLZPj6Aggn.jpg)
 Deutsch
Deutsch Русский
Русский Українська
Українська English
English Italiano
Italiano Français
Français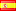 Español
Español 汉语
汉语





-300-150-qGsKX9ISubMAAAFaDA5MgKnU.jpg)







